Graph Cut Segmentation and Background Removal
Have you ever wanted to cut out a specific object from a photo but found manual selection tools tedious and inaccurate? This challenge is known as Foreground Extraction. Simple thresholding often fails because real-world objects have complex colors and lighting. To solve this, we use an advanced iterative algorithm called Graph Cut Segmentation.
How Graph Cut Works (In Simple Terms)
Imagine you are trying to cut a sticker out of a magazine. You draw a rough box around the object. You tell the computer: "Everything outside this box is definitely background. Everything inside is unknown." The Graph Cut algorithm then acts like a smart painter. It looks at the colors outside the box to learn what "background" looks like. It then scans the inside of the box and tries to separate pixels that match the background from those that look unique (the foreground).
Example: Background Removal
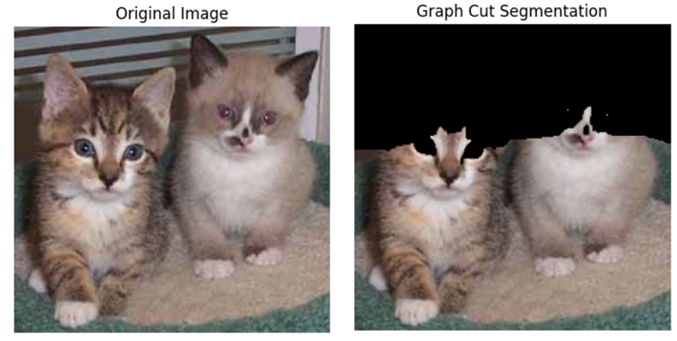
Mathematical Explanation (Graph Theory)
Graph Cut treats the image as a Graph, where every pixel is a node. The algorithm uses a technique called Graph Cut (Min-Cut/Max-Flow). It models the colour distribution of the Foreground and Background using Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs).
The energy function E is minimized to find the best cut:
- U (Data Term): How likely a pixel belongs to the Foreground or Background based on its colour.
- V (Smoothness Term): Penalizes cutting through regions of similar colour (encouraging the cut to follow high-contrast edges).
Read the engineering docs to understand the implementation of Graph cut Segmentation.
Read Technical Docs →Why Use Graph Cut?
- High Accuracy: Handles complex textures better than simple colour thresholding.
- Minimal User Input: Requires only a rough bounding box, not precise drawing.
- Iterative Refinement: The algorithm "learns" and improves its mask with each loop.
- E-Commerce: The industry standard for automatically removing backgrounds from product photos.